We have a passion for unconventional solutions that bring your vision to life.
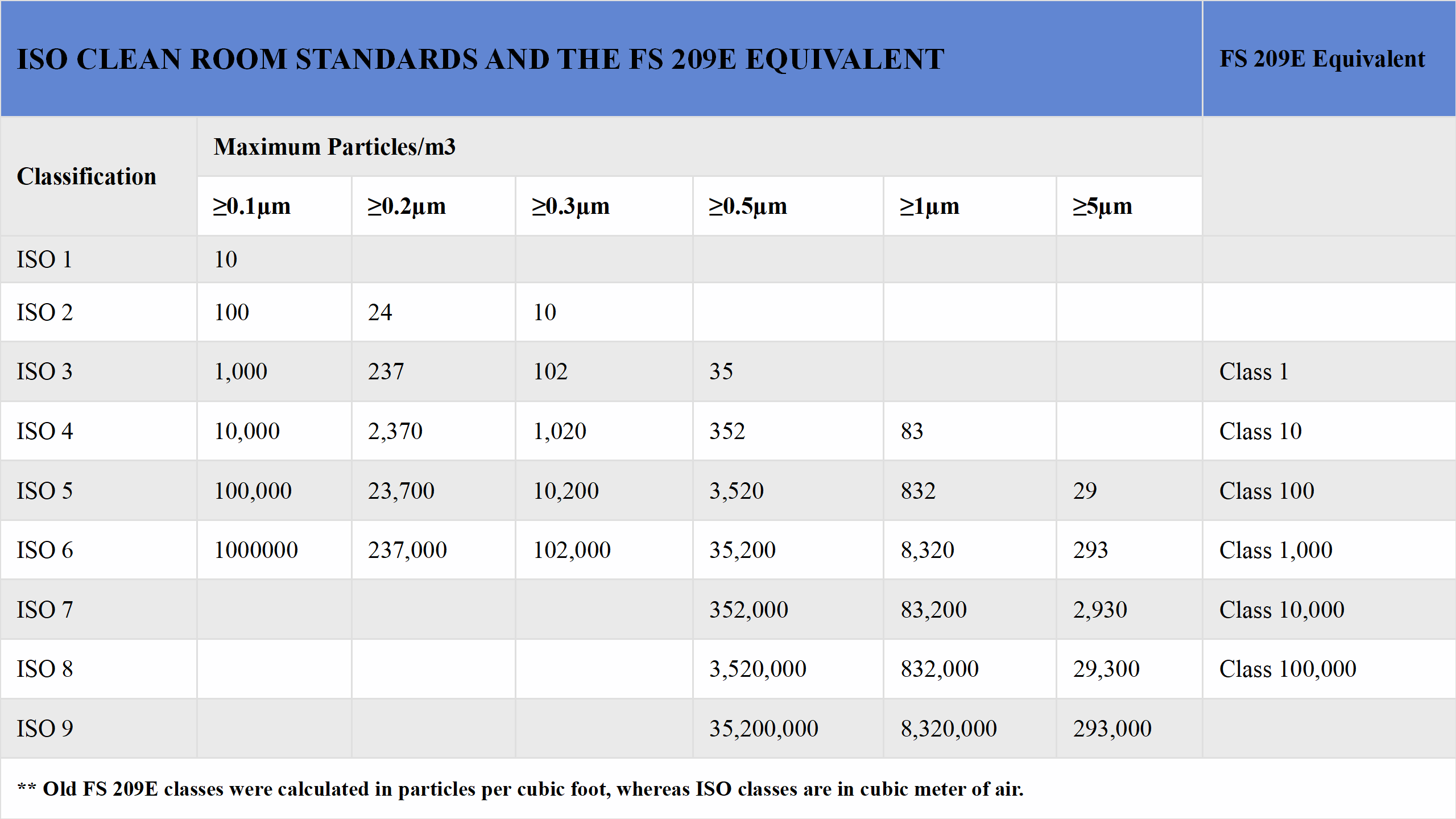
Cleanrooms are specialized environments engineered to maintain extremely low levels of airborne particulate matter, creating optimal conditions for sensitive industrial and research processes. These spaces are governed by the ISO 14644-1 standard, which categorizes cleanrooms from ISO 1, the cleanest, to ISO 9, the least clean, based on specific limits for particle concentration. To achieve such high cleanliness levels, cleanrooms utilize high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters, which cycle air multiple times per hour to eliminate contaminants. For instance, an ISO 5 cleanroom requires 240–360 air changes per hour, while an ISO 6 needs 90–180. Each cleanroom is custom-designed, taking into account factors such as room size, operational workflows, and equipment requirements. In the following content, we will have a detailed exploration of ISO 5 cleanrooms.
The ISO 14644-1 standard establishes cleanroom classifications by defining the maximum allowable concentration of particles per cubic meter for specific particle sizes, such as those ≥0.5 µm. An ISO 5 cleanroom, for example, permits no more than 3,520 particles of ≥0.5 µm per cubic meter, making it significantly cleaner than ISO 7 or ISO 8 environments. Commonly referenced classifications include ISO 7 and ISO 8, which align with the older Federal Standard 209E's Class 10,000 and Class 100,000, respectively.This standard operates on a logarithmic scale, where each classification level represents a tenfold decrease in particle concentration. Unlike the older Federal Standard 209E, which measured particles per cubic foot, ISO 14644-1 uses the metric system for global consistency. Compliance with these standards requires rigorous testing, including particle counting, airflow measurements, and pressure differential checks, to ensure the cleanroom consistently meets its designated classification.
ISO 5 cleanrooms are critical in industries where contamination control is paramount. These highly controlled environments maintain stringent air quality standards, ensuring product integrity, safety, and performance across various sectors.
In semiconductor production, ISO 5 cleanrooms are indispensable for processes like photolithography, where microchips are fabricated with nanometer-scale precision. Even a single dust particle or microscopic contaminant can disrupt circuit patterns, leading to defective chips and significant financial losses. The semiconductor cleanroom employs advanced filtration systems, such as HEPA or ULPA filters, and maintain laminar airflow to minimize particle presence. They are also used in wafer fabrication, chip assembly, and testing, ensuring high-yield production of microprocessors, memory chips, and other integrated circuits critical to electronics.
ISO 5 cleanrooms are vital in the production and packaging of medical devices, particularly for critical implants like pacemakers, stents, and orthopedic prosthetics. These environments ensure sterility during final cleaning, assembly, and packaging, preventing contamination that could lead to infections or device failure in patients. For example, during the assembly of intraocular lenses or surgical tools, medical clean room eliminates airborne particulates and microbes, adhering to strict regulatory standards like those set by the FDA or EU MDR. The controlled environment also supports quality assurance testing, ensuring devices meet biocompatibility and performance requirements.
In the pharmaceutical industry, ISO 5 cleanrooms are essential for aseptic processing, particularly in the production of sterile injectable drugs, such as vaccines, biologics, and chemotherapy agents. Pharmaceutical cleanrooms facilitate critical processes like aseptic filling, lyophilization, and vial sealing, where microbial contamination could compromise drug safety and efficacy. They are equipped with advanced HVAC systems and environmental monitoring to maintain sterility and comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). ISO 5 cleanrooms also support the production of sterile ophthalmic solutions and inhalation therapies, ensuring patient safety and regulatory compliance.
ISO 5 cleanrooms are also widely used in pharmaceutical compounding to prepare sterile medications, such as customized IV solutions, chemotherapy drugs, or compounded biologics. These cleanrooms ensure that medications are free from microbial contamination, protecting immunocompromised patients and meeting USP <797> standards. Pharmacists and technicians work in ISO 5 laminar airflow hoods within these cleanrooms to compound sterile preparations, ensuring precision and safety in drug formulation.
Aerospace organizations, including NASA and private space companies, rely on ISO 5 cleanrooms for the assembly and testing of satellites, spacecraft components, and precision instruments. For instance, during satellite assembly, even minute particles can interfere with optical systems, sensors, or solar panels, potentially causing mission failures. ISO 5 cleanrooms ensure a dust-free environment for manufacturing gyroscopes, telescopes, and other sensitive equipment. They are also used in the calibration and testing of aerospace components, where contamination could affect performance in the harsh conditions of space.
Universities, national laboratories, and research institutions utilize ISO 5 cleanrooms for cutting-edge research in fields like nanotechnology, optics, and biotechnology. In nanotechnology, these cleanrooms enable the manipulation of materials at the atomic or molecular level, where contaminants could alter experimental outcomes. For example, cleanrooms are used to fabricate nanoscale sensors or quantum devices. In optics, ISO 5 environments ensure dust-free conditions for developing high-precision lenses and laser systems. Biotechnology research, such as gene editing or cell culture studies, also relies on these cleanrooms to maintain sterile conditions and prevent cross-contamination.
In the production and repair of hard disk drives (HDDs), ISO 5 cleanrooms are critical to maintaining the precision and reliability of storage devices. Dust particles or contaminants can cause read/write errors or damage delicate components like magnetic platters or read heads. These cleanrooms are used during assembly, testing, and repair processes to ensure defect-free production. As data storage demands grow, ISO 5 cleanrooms remain essential for manufacturing high-capacity HDDs and solid-state drives (SSDs) with nanometer-scale components.
The materials used for walls, floors, and ceilings must be smooth, non-porous, and resistant to chemical cleaning agents, with stainless steel or epoxy-coated surfaces often chosen to prevent particle shedding. High-efficiency HEPA filters, typically installed in the ceiling or walls, deliver laminar airflow to ensure uniform air distribution and rapid contaminant removal. The airflow design emphasizes unidirectional flow, maintaining a consistent speed of approximately 0.45 m/s ±20% to minimize turbulence. The room layout incorporates airlocks, gowning rooms, and pass-throughs to prevent external contamination, while positive pressure systems keep unfiltered air out. Environmental controls are also critical, with temperature maintained between 20–22°C and humidity levels kept at 40–60% to optimize equipment performance and prevent static buildup.
Maintaining an ISO 5 cleanroom requires strict protocols to ensure ongoing compliance with cleanliness standards. Surfaces are cleaned daily with approved disinfectants using techniques that avoid generating additional contaminants, ensuring the removal of particles and microbes. Particle monitoring is conducted continuously or periodically with laser particle counters to verify that particle concentrations remain within ISO 5 limits. Regular testing of air change rates and pressure differentials ensures that HEPA filters and ventilation systems function optimally. Personnel undergo extensive training in gowning procedures, aseptic techniques, and behaviors designed to minimize contamination risks, such as avoiding rapid movements that could stir up particles. ISO 5 cleanrooms also undergo regular certification, typically annually, per the ISO 14644-1 standard, involving comprehensive tests of particle levels, airflow, and other environmental parameters to confirm compliance.
What Is an ISO 8 Cleanroom Classification?
What Is an ISO 7 Cleanroom Classification?
What Is an ISO 6 Cleanroom Classification?

Wiskind Cleanroom specializes in cleanroom enclosure system , ceiling system, cleanroom doors and windows and related product development, manufacturing, sales, consulting and services.