We have a passion for unconventional solutions that bring your vision to life.
ISO Class 8 cleanrooms are the workhorses of contamination control—widely used in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to electronics. They offer a practical balance of cleanliness and cost efficiency, providing the right environment for processes that don't require the extreme sterility of higher ISO classes but still demand controlled conditions.
ISO Class 8 cleanrooms are controlled environments that limit airborne particles to protect sensitive processes and products. According to ISO 14644-1, these rooms must not exceed 3,520,000 particles ≥ 0.5 microns per cubic meter (equivalent to about 100,000 particles per cubic foot) and allow no more than 29,300 particles ≥ 5 microns per cubic meter.
To maintain this cleanliness level, ISO 8 cleanrooms typically require around 20 air changes per hour (ACH) using HEPA-filtered air delivered through clean room FFU (fan filter units) mounted in the ceiling grid to continuously remove contaminants. Every design element—from ceiling filters to return vents—is planned to keep particulates under tight control.
For comparison, a typical office environment contains roughly ten times more airborne particles than an ISO 8 space, demonstrating just how controlled these environments are.
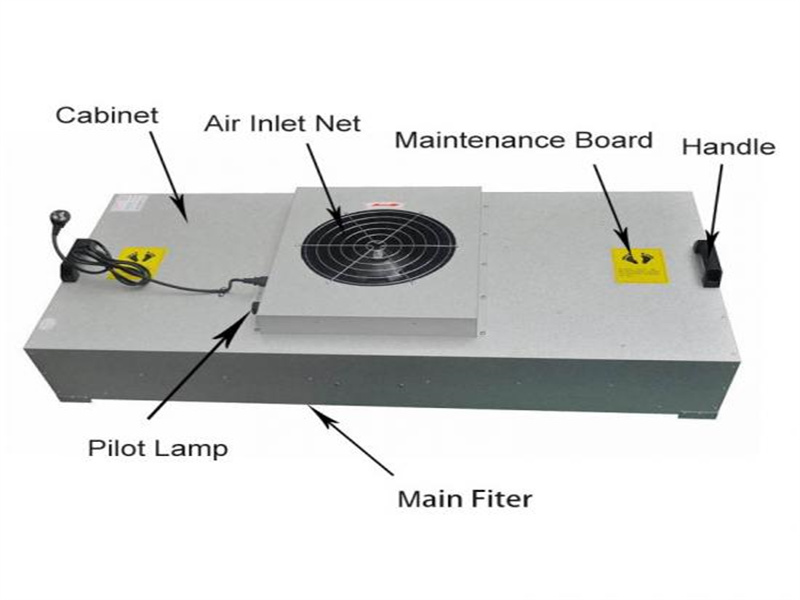
An ISO Class 8 cleanroom provides a moderately controlled environment ideal for industries that require cleanliness without the extreme measures (and costs) of higher-class facilities. Common applications include:
· Pharmaceutical manufacturing: secondary packaging and storage areas where sterility isn't critical but cleanliness still affects quality.
· Food and beverage processing: areas where particulate control supports hygiene and product safety.
· Electronics and optics production: assembly tasks where even small dust particles can damage sensitive components.
· Medical device assembly: preventing contamination that could compromise product reliability or sterility assurance.
Essentially, ISO 8 cleanrooms deliver the practical middle ground between cost-efficiency and cleanliness—perfect for mid-sensitivity production and testing processes.
The key difference between ISO 7 and ISO 8 cleanrooms lies in their allowed particle count and air change rate:
· ISO Class 7: Allows up to 352,000 particles ≥ 0.5 microns per cubic meter and typically requires 60 ACH.
· ISO Class 8: Permits up to 3,520,000 particles ≥ 0.5 microns per cubic meter with about 20 ACH.
Because ISO 7 environments have stricter limits and a higher air exchange rate, they're typically used for higher-risk operations such as aseptic filling, pharmaceutical compounding, or microelectronics fabrication. In contrast, clean room ISO 8 environments support less critical processes or serve as intermediate zones, such as gowning, material staging, or buffer areas connected to cleaner ISO 7 spaces.
Yes. Under EU GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) classification, Grade D equates to ISO Class 8. The full cross-reference between GMP and ISO standards follows this general framework:
· Grade A = ISO Class 5 (used for sterile filling or laminar airflow zones)
· Grade B = ISO Class 5 background / ISO 7 support
· Grade C = ISO Class 7 or 8 (depending on activity)
· Grade D = ISO Class 8 (used for less critical manufacturing steps such as non-sterile component preparation)
This alignment ensures global consistency, allowing facilities to meet multiple regulatory systems seamlessly.
To meet ISO 8 classification, cleanrooms must follow specific engineering and operational requirements, including:
· Air cleanliness: Fewer than 3,520,000 particles ≥ 0.5 µm/m³ and 29,300 particles ≥ 5 µm/m³.
· Ventilation rate: Minimum 20 air changes per hour, using HEPA or ULPA filtration.
· Environmental parameters: Controlled temperature (18–23 °C) and humidity (40–60%) for stability and comfort.
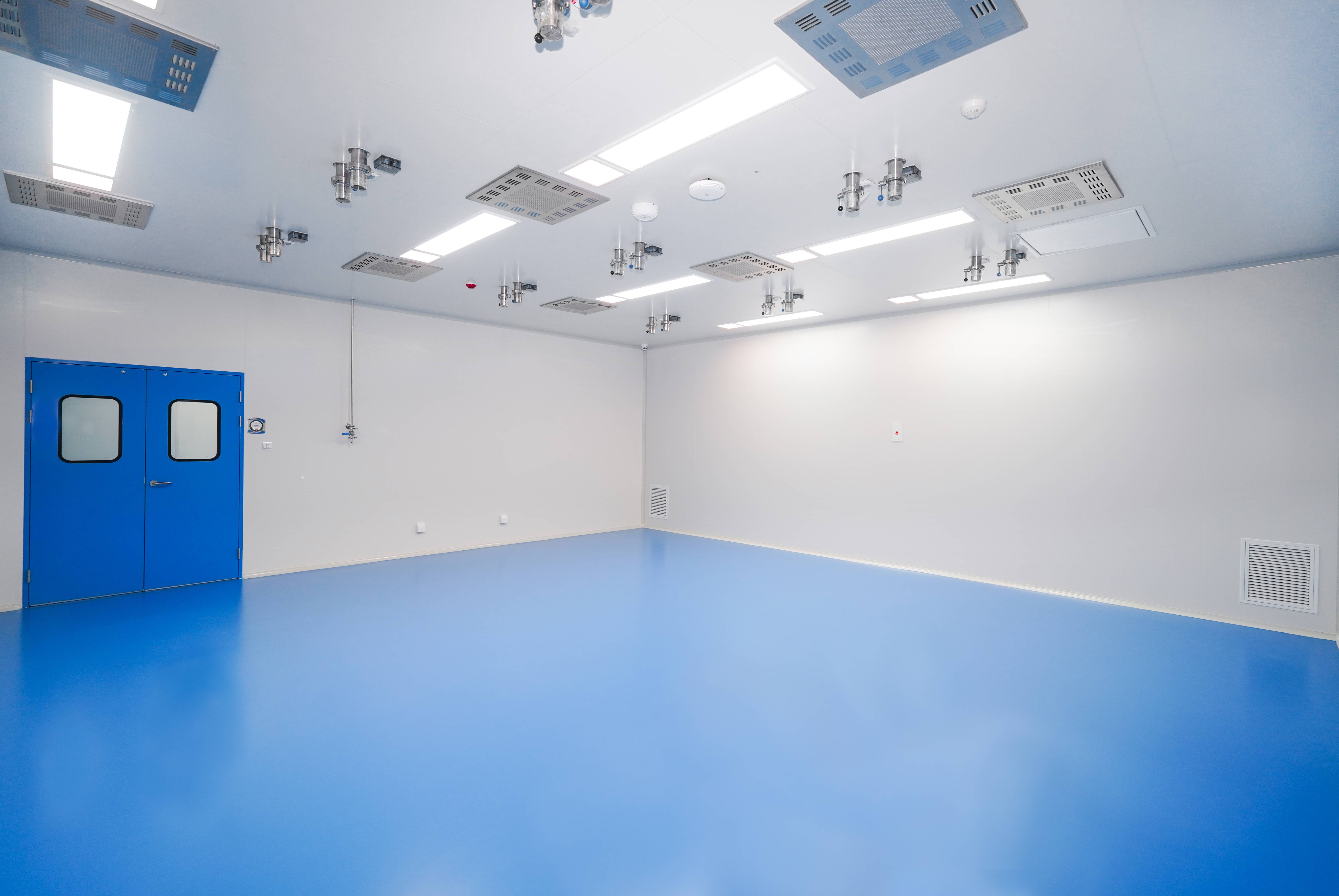
· Surface requirements: Smooth, non-porous, easy-to-clean materials that reduce particle shedding. Modern clean room wall panel systems (often modular sandwich panels with stainless steel or coated surfaces) and clean room windows with double-glazed, flush-mounted designs are commonly used to create durable, hygienic boundaries.
· Storage & organization: Clean room cabinets with laminar flow or sealed construction help maintain cleanliness while providing secure, accessible storage for tools, garments, and materials.
· Operational protocols: Proper personnel gowning, cleaning procedures, airlocks, and continuous particle monitoring.
Together, these measures ensure a clean, controlled, and reproducible environment that safeguards product integrity and regulatory compliance.

ISO sets quality and safety benchmarks across nearly every global industry. While there are thousands of ISO standards, these five are among the most widely recognized and applied:
· ISO 9001 – Quality Management Systems: Ensures consistent product quality and customer satisfaction.
· ISO 14001 – Environmental Management: Guides organizations in minimizing environmental impact.
· ISO 27001 – Information Security: Protects sensitive data and mitigates cybersecurity risks.
· ISO 45001 – Occupational Health & Safety: Promotes safer work environments and reduces accidents.
· ISO 22000 – Food Safety Management: Secures food safety from production to consumption.
Together, these standards reinforce trust, compliance, and continuous improvement—principles that also drive the meticulous discipline required in ISO 8 cleanroom facilities.

Wiskind Cleanroom specializes in cleanroom enclosure system , ceiling system, cleanroom doors and windows and related product development, manufacturing, sales, consulting and services.